
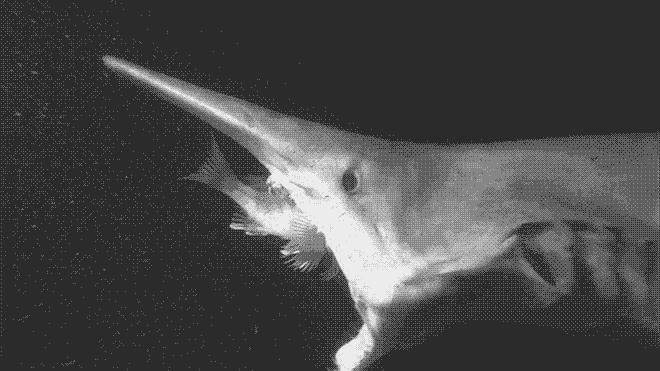
It’s known that the goblin shark swims in deep water. This suggests that they feed mainly on soft prey: small fish, octopus, squid, and shrimp.

The shape of their thin and narrow teeth are shaped like a hole punch, and their posterior teeth are desgined for grinding. When they find a prey, the jaw projects forward in the form of a catapult. The strong ligaments of the mandibular joints keep them tight while swimming. Their jaws are conditioned for a rapid projection and thus this is how they capture their prey. With this, they are able to electronically detect the prey. The goblin shark uses special sensing organs called the Ampullae of Lorenzini that are located on their snout. Information on their life expectancy is unknown.When it comes to their reproduction process, they are likely to be ovoviviparous and they reach their sexual maturity once the males measure around 8.5 feet in length.
EVERBLUE 2 GOBLIN SHARK SKIN
They have very small eyes because they swim in very deep waters, and their skin is protected by structures called dermal denticles.The average weight of an adult goblin shark is 463 pounds.However, females can reach up to 20 feet in length.

They measure between 9.8 and 13 feet in length.

Its primitive features give it its second name, the living fossil. It’s a fish called elasmobranch lamniform and is the only living specimen of the Misukurinidae family. Do you want to learn about this magnificent creature? Below, are this animal’s main traits. The new findings on once shallow-water-dwelling sharks are likely to have a strong impact on future studies relating to how fish adapt to deep-sea environments.The goblin shark is a rather peculiar species because its large V-shaped snout makes it stand out and it reminds us of extinct animals. Until now, few details were known about the species. Known as Mitsukuri sharks in Japan, goblin sharks are so called in Western nations due to their somewhat alarming appearance: a pinkish body lacking proper pigment, exposed teeth and protruding jaws. The researchers concluded that the shark, which has a slow swimming speed, has evolved to adapt to deep-sea environments where food is scarce, possibly compensating for its slow swimming speed. The researchers also newly discovered that the sharks opened and closed their mouths again during jaw-retraction, for unknown reasons. The biting process, named "slingshot feeding" by the researchers, involved the projection of the jaws at speeds of up to 3.1 meters per second - the fastest speed recorded for a fish - over distances comparable to 8.6-9.4 percent of the total length of the shark's body, far outranking the jaw protrusion of other kinds of shark. The goblin shark ( Mitsukurina owstoni) was first discovered in deep waters off Japan in 1898.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
